Tinea is the term used to describe a group of contagious skin infections caused by different type of fungi.
Dermatophytes are a group of organisms that are able to breakdown the skin tissues.
Dermatophytosis is mainly caused by microsporum, trichophyton and epidermophyton.
These dermatophytes grow best in warm and humid environments.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF TINEA INFECTIONS
It affects many areas of skin and depending on thier location and fungal infection it has different names.
Common type of Dermatophytosis depending on the sites are as follows
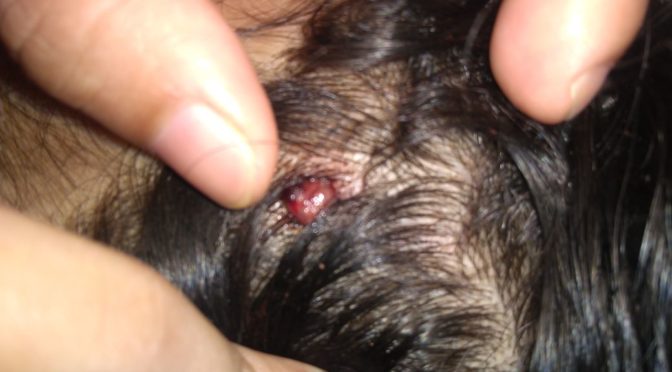
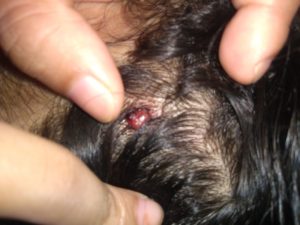
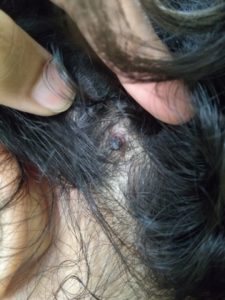
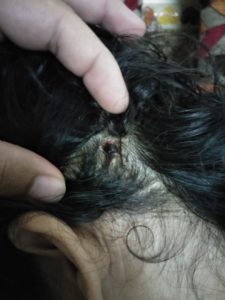
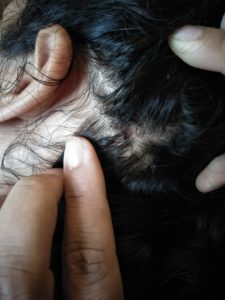
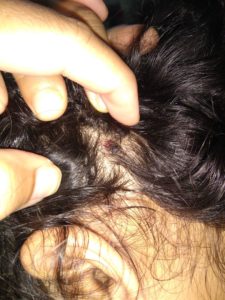
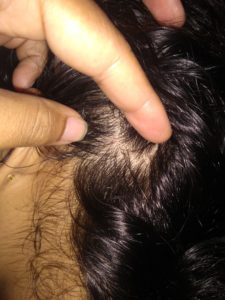
TINEA CAPITIS
Scalp ringworm causes itchy patches on the head, it can leave bald spots, usually affects children.
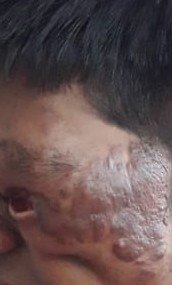
TINEA BARBAE
It is the infection of the skin especially beard area and moustache and is usually seen in men.
TINEA CRURIS
It is also known as Jock’s itch. Infection of groin, vulva, inner thighs , buttocks.
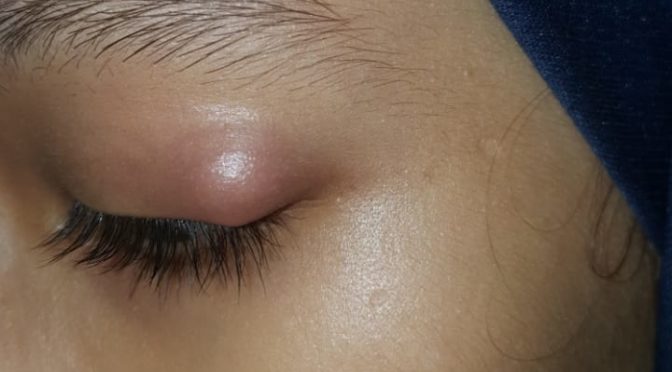
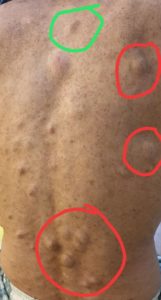
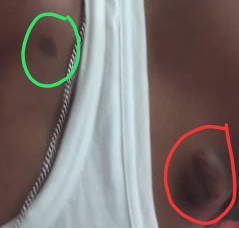
TINEA CORPORIS
When Dermatophystosis presents on the parts of body like trunks, hands, feet etc.
TINEA UNGUIUM
It is infection of one or more finger nails or toe nails.
TINEA PEDIS
It is also known as Athlete’s foot, causes infection of the foot or inter digits of foot.
CAUSES OF TINEA INFECTIONS
Dermatophytosis are the group of organisms that are able to break down the skin tissue. The fungi reside in the soil and are involved in decomposition and can infect the living organisms.
Dermatophytes are transmitted from person to person and some are adapted to animals.
Dermatophytosis is mainly caused by microsporum, trichophyton and epidermophyton. These dermatophytes grow best in warm and humid environments.
It can be easily transmitted through skin to skin contact with an infected person or animal or through indirect contact with an object or surface that an infected person or animal has touched.
Bathroom floors, bathmaths, towels, showers and communal bathing, swimming and changing room areas are common source of infection.
On contact with skin, the dermatophyte spread to the surface layers of the skin.
SYMPTOMS OF TINEA INFECTION
Symptoms of the fungal infections vary depending upon the infection and affected tissues and area of the body.
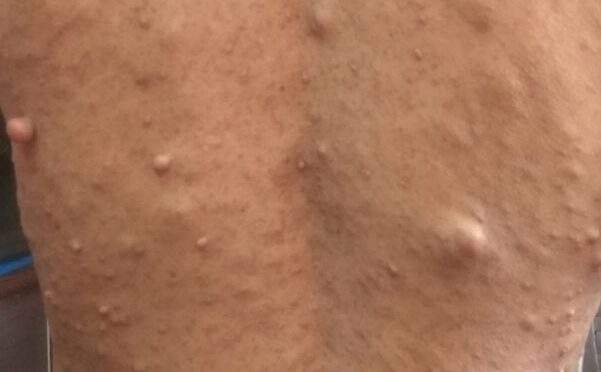
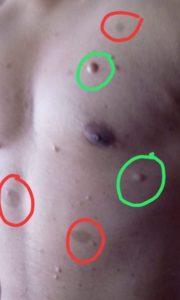
The skin lesions are usually characterised by redness, inflammation that is more severe at the edges with raised and thick edges, it is usually seen that the central area is clear.
SYMPTOMATIC REPRESENTATION OF TINEA DEPENDING ON THE AFFECTED SITE
TINEA CAPITIS
Tinea Capitis is also known as scalp ringworm. It usually affects children. Seen in children with infection of hair and scalp. The infection is characterised by scaly, irregular or well marked redness with patchy hair loss, the patchy areas are dry with loss of hair and minimal inflammation.
TINEA BARBAE
The dermatophytic infection that involves hair and skin of the face that is the beard and moustache. The lesions may include scaling with pus along with redness.
TINEA FACIEI
It is seen on non beard parts of the face.
TINEA CRURIS
This is an acute to chronic infection of the groin and adjacent areas like inner thighs, butocks. The symptoms usually imclude burning, severe itching and redness with scales, raised edges, sharply demarcated borders with clear centre. Skin becomes dark in the centre as the lesion progreses.
TINEA CORPORIS
Tinea Corporis occurs on the trunk, hands and feet. The infection usually tends to spread to other areas. The lesions are usually pink to red or scaly and annular with slightly raised and sharp margins with clear centre. Sometimes lesions may present with pus.
TINEA UNGUIUM
Tinea Unguium is infection of nails characterised by thickened opaque, a discoloured or deformed nails. The nail may be separated from nail bed. Toe nails are more affected than finger nails.
TINEA PEDIS
Tinea Pedis is seen between the digits of feet. Commonly called as athlete’s foot. There is dryness, fissures and scales, moist lesions in some or all spaces. The lesions may be present with scaling of the soles with inflammation and dryness or redness.
ROLE OF HOMEOPATHY IN TINEA INFECTIONS
Homeopathic treatment is very beneficial and effective mode of treatment that boosts the bodys immune process to fight and eradicate fungal infections.
As the infection gets older, it tends to get more resistant to any form of treatment, once external applications are used for months together the infection becomes resistant. Homeopathy plays an important role in such cases.
INDICATED HOMEOPATHIC REMEDIES
SULPHUR
Sulphur is very beneficial homeopathic medicine for various skin diseases. In cases of ring worm lesions sulphur is quiet useful.
The patient presents with intense itching and burning in erruptions. Indicated in cases of infections that have been suppressed by local medications of various kinds.
PSORINUM
Psorinum is one of the indicated remedy for skin infections. Mainly used for ringworm infections of scalp and bends of joints. There is severe itching in the affected area. Itching worse due to warmth of bed. Indicated in tinea capitis. The hair appears dry, rough, and lustreless. Profuse sweating with offensive body odour throughout the body.
SEPIA
Indicated in case of fungal infections appearing in isolated parts of body. Infections can occur on any part of the body, but common location is bends of knees and elbow. The erruptions are accompanied by itching and scratching, no relief from scratching. High senditivity towards cold air.
Irritable, indifferent towards family and friends.
THUJA
Thuja is indicated in skin infections. Main action is on skin. Indicated in case of dermatophytic infection where the erruptions are on the covered parts of the body, worse from scratching, very sensitive to touch. Worse at night from heat of bed, from cold damp air. Scratching and cold bathing makes the condition worse.
GRAPHITES
Graphitis is one of the indicated remedy for jocks itch Tinea Cruris with recurrent episodes. Indicated where the skin is dry, rough with severe itching. Sometimes moist crusty erruptions are seen on the parts. There is oozing of sticky exudation. Graphitis is effective for fungal infection around vulva.
ARSENIC ALBUM
Arsenic album is beneficial in Tinea Capitis. The scalp shows bald spots with intolerable itching with intense burning. The symptoms are usually worse at night. Arsenic alb helps to reduce itching and burning and also helps in regrowth of hair on bald spots.
SILICEA
Silicea is indicated in Fungal infections and dermatophytosis in Delicate pale waxy patient. Scars are painful. Eruptions itch only in the day time and evening. Crippled nails. Indicated in case of Tinea Pedis with offensive sweat, deep cracks between toes with intense itching and burning. Painful foul smelling ulcers of the foot.
PERTROLEUM
Petroleum is indicated in case of Tinea Pedis. Helps to drive away infection of foot. Presents with offensive sweat. Deep cracks between toes with intense itching and burning of skin. Crippled and brittle nails.
TELLURIUM
Tellurium is indicated in Dermatophytosis with lesions on large parts of the body. Usually it covers a broader area of skin. Presents with excessive itching and stinging sensation. Itching day and night. Cold air worsens the itching. Offensive odour from the affected area.