Psoriatic Arthritis is a condition found in patient suffering from autoimmune disease called Psoriasis where in there is involvement of joints as well, along with skin and nail. It is classified as Seronegative Arthropathy and individuals with HLA B27 genotype shows more susceptibility towards this condition with genetic and environmental factors playing a major role in precipitation of the condition.
It presents itself as Chronic Inflamatory Arthritis involving one or more joints which accompanies or alternates with acute of spells of Psoriasis or has relation with the cyclic pattern of Psoriasis.
Signs and Symptoms of Psoriatic Arthritis
If a person is suffering from Psoriasis doesnt mean he will develop psoriatic Arthritis, regardless of severity of psoriasis he is suffering from. But its observed that person having Psoriatic Arthritis shows some relation between skin complaints and joint complaints either they aggravate together or alternate each other in their spells of aggravation but not in every case and always.
70% of Psoriatic Arthritis cases presents first sign of disease as psoriasis lesion on skin, in majority cases it usually develop almost 10yrs after onset of appearance of skin psoriasis. majority of them are adults between 35-55yrs.
15% first develops joint complaints then skin psoriasis develops later. and majority of them are children.
15% presents both skin and joint complaints originating simultaneously at the onset of disease.
SKIN and NAIL
Typical features of Psoriasis on Skin and Nail
- Silverish scaly skin exfoliating cyclically leaving behind clear red base on extensor surface of skin and typically on scalp, around umbilicus.
- Exudation and cuts may also be seen in severe cases.
- Onycholysis, Ridges on nail, Pitting on nail, Hyperkeratosis of skin below nails of fingers and toes.
MUSCULOSKELETAL
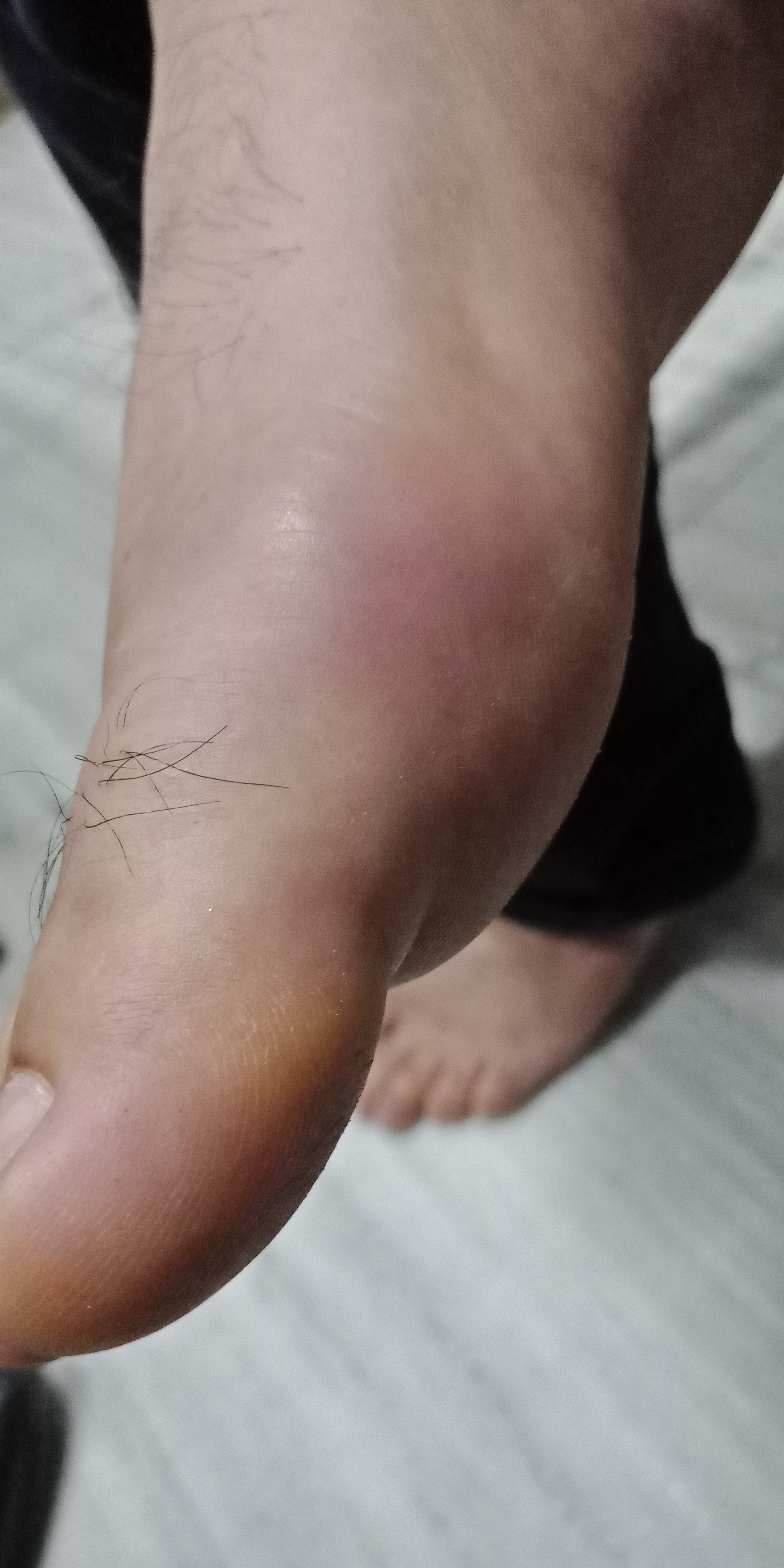
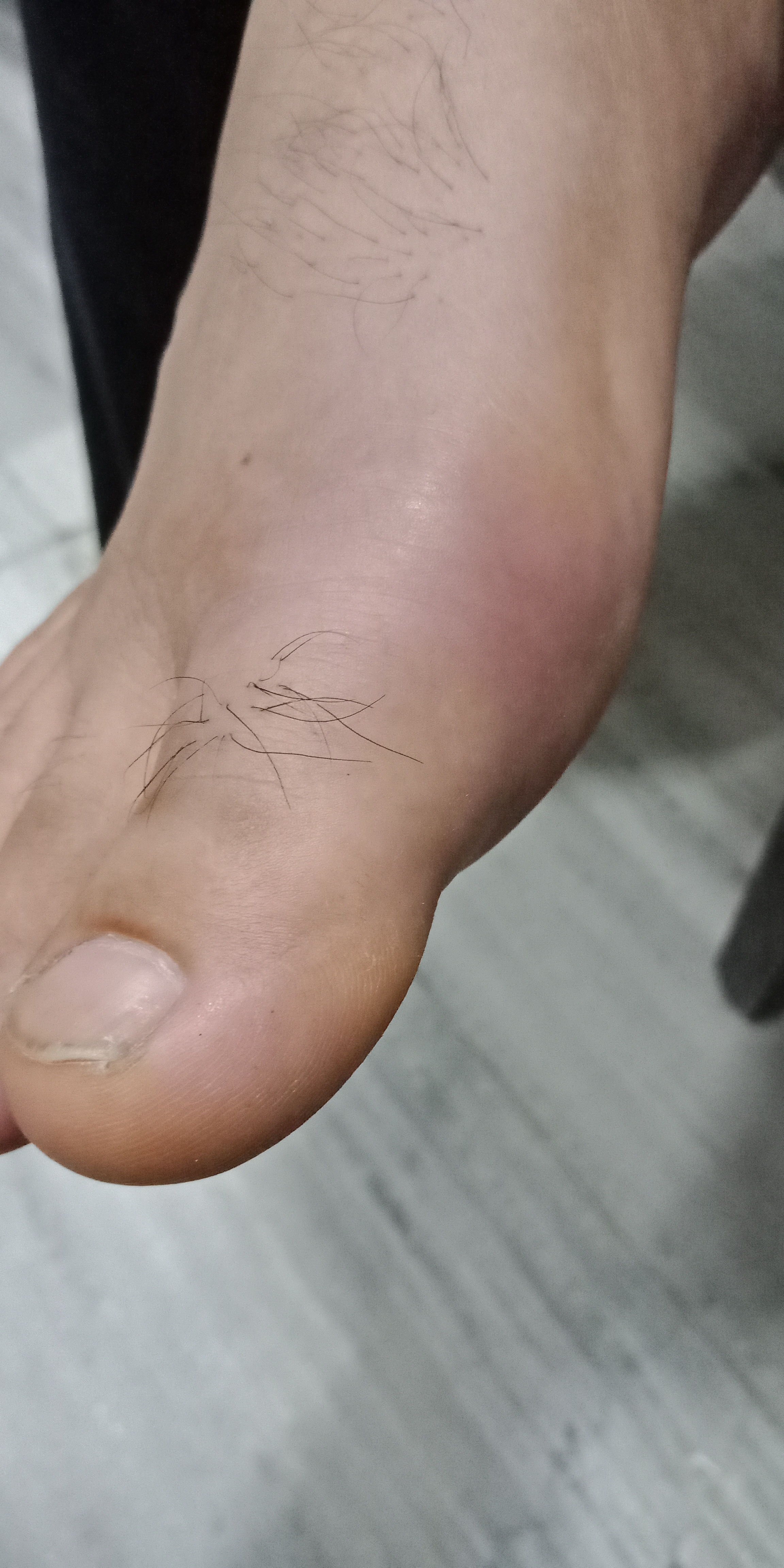
It more frequently involves small joints of hand and feets especially of Fingers and Toes frequently wrist and spine are also involved, There is morning stifness pain and swelling of joints. Almost 20% cases shows symetry in joints involved.
- Swelling of fingers, Dactilitis, giving sausage like appearance to fingers.
- Sacroilitis, Lumbar spondylitis, pain in lower back
- Cervical Spondylitis, pain in cervical region.
- Enthesitis of Tendo-Achilles causing severe pain in ankle.
- Plantar Fascitis causing pain and stiffness in soles.
GENERAL
When the disease progresses or aggravates patient may show signs of
- Malaise, Fatigue Weakness and Exhaustion.
- Deformities, Disfigurement and Disabilities.
- Anaemia of Chronic Disease.
Psoriatic Arthritis presents itself in one of the following five patterns.
1) Oligoarticular
Its the most common type affecting almost 70% of all the cases where in ther is involvement of less than 3 joints and lacks symetry.
2) Polyarticular
Its comparatively severe type and accounts for almost 25% of all the cases of which 50% develops disability and deformities. It typically involves more than 4-5 joints and shows somewhat symetrical pattern. It resembles much to Rheumatoid Arthritis and need to differentially diagnosed which becomes difficult in sero-negative Rheumatoid Arthritis cases.
3) Arthritis Mutilans
Also called Chronic Absorptive arthritis ans is found in almost 5% of all the cases and is the most severe and destructive form of arthritis presented due to psoriasis and in many other conditions like Rheumatoid Arthritis and it shows severe disfigurement and deformities.
4) Spondyloarthritis
Typically affects spine especially the cervical spine and sacro-illiac joint. may also affect other joints as well in a symetric fashion.
5) Distal Interphalangeal
Typically involves distal small joints of fingers and toes with involvement of nails.
Diagnosis of Psoriatic Arthritis
There is no Specific Test Available For Psoriatic Arthritis. It cant be predicited based either only on joint or only on skin complaints that the person is developing Psoriatic Arthritis and its only after both skin and musculoskeletal complaints presents itself the diagnosis can be established. So, early diagnosis is not possible and its usually established only after the disease has progressed enough to show itself on both the spectrums.
The diagnosis of Psoriatic Arthritis depends upon clinical features and host of investigative tests that collectively exclude probability of other conditions and indicate towards Psoriatic Arthritis.
- Psoriasis with chronic inflamatory arthritis of which the aggravation pattern can be related to cyclic process of psoriasis but not necessarily in all cases. Especially showing features like
- Distal interphalangeal arthritis
- 80% of patients presents nail complaints Onycholysis – ridging pitting and hyperkerotosis of skin under nail
- Dactilitis, sausage like appearance of fingers.
- 30-50% patients show Enthesitis, involving Tendo-Achilles, Plantar fascia,
- Pain around Patella, illiac crest, epicondyles, supraspinatus insertions, sacroillitis.
- X ray shows degenerative changes
- Family history of psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis
- Subjects with HLA B27 genotype.
- Negative Serological tests like RA factor and ACCP of Rheumatoid Arthristis.
For Differential Diagnosis of Psoriatic Arthritis Read
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
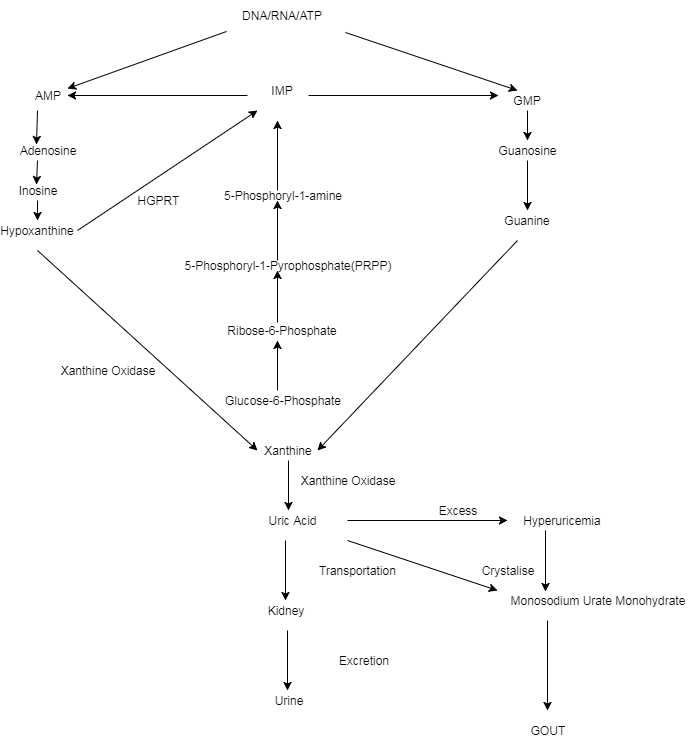
- Gouty Arthritis
- Ankylosing Spondylosis
- Osteoarthritis
- Inflamatory Bowel Disease related Arthritis
- Systemic Lupus Erythematousus
Homoeopathic Treatment For Psoriatic Arthritis
As mentioned above its an autoimmune condition chronic in nature. So its important to treat the cause first and the symptoms will be relieved on its own. For that a proper homoeopathic case taking and constitutional approach is necessary as its deep seated genetic complaint and only a deep seated constitutional remedial force can bring about change for better. But in many severe cases where there are gross degenerative changes or the disease has progressed much further or the pain is severe we need to treat theraputically initially to get the acute exacerbations in check and later we can find out constitutional remedy based on Miasmatic background and totality of symptoms of Mind and Body. Also There arise much need for anti-miasmatic nosode administeration in the course of treatment if the case is improving but improvement is soon regressing or case has hit a stand still and ia not reaponding further in such case we need to consider a nosode.
Homoeopathic Medicines for Psoriatic Arthritis
RHUS TOX
Rhus tox is usually adapted or well suited to a person of rheumatic diathesis. Rhus tox is very well indicated in psoriatic arthritis. The effects on the skin, rheumatic pains, mucus memmbrane affections makes this remedy frequently indicated. Rhus tox affects the fibrous tissue of the joints, ligaments causing rheumatic symptoms. Patient presents with burning eczematous erruptions with tendency to scale formation. Skin is red swollen with intense itching. Hot painfull swelling of joints. Rheumatic pains spread over a large surface area at nape of neck, loins, and extremities which is relieved by motion. The cold fresh air is intolerable makes the skin painful.
URTICA URENS
Urtica urens is one of the indicated remedy for psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatism is usually associated with skin complaints. As its common name stinging nettle implies it produces stinging and burning pain. Skin complaints alternate with rheumatism with severe pain in joints. Itching and swelling all over body resembling hives. Heat in skin of face arms shoulderand chest with formication numbness and itching. Psoriatic errruptions with scales, skin looks wrinkled. Intense burning of skin. Patient is worse from exposure to cold moist air.
RHUS VENETA
In case of Rhus veneta, the skin symptoms of this species of rhus are most severe. Rhus veneta is one of the most actively poisonous remedy among the family. Presents with great restlessness.,numbness and lameness of joints. Bruised feeling in the limbs. Pains as if sprained or dislocated. Presents with trembling of limbs with twitching of muscles. Rashes under the skin with severe nightly itching. Fine psoriatic erruptions on forearm, wrist, back of hands between and on fingers. Severe desquamation with severe itching. Complaints are usually aggravated by warmth.
LEDUM PAL
Ledum pal usually affects the fibrous tissue of joints especially small joints. Hence it can be called as a rheumatic remedy where rheumatism begins in the feet and travels upwards. Ledum pal is very valuable remedy in psoriatic arthritis. There is weakness and numbness of affected parts. Painful cold oedematous joints. Presents with erruptions only on the covered parts of the body. Affecting the skin ledum produces reddish spots with scaly erruptions. Gouty pains shoot all thrkugh the foot and limbs. Cracking in joints worse from warmth of bed. Aggravation from warmth is so severe that the patient can only get relief from rheumatism is by putting his feet in cold water.
BELLADONA
Belladona has marked sphere of action on the skin, bones, glands and nervous system. Useful in case of psoriatic arthritis. Pains are usually throbbing, sharp, cutting, shooting which come and go in repeated attacks. Joints are swollen, red hot with severe throbbing sensation and extreme sensitiveness. The heat, redness and burning characterise most of the skin complaints, and presnts with alternate redness and paleness of skin with scaly erruptions and severe itching. The complaints of belladona come on suddenly, eun a regular course and subside suddenly.
SILICEA
Silicea too can be considered one of the efficient remedy in psoriatic arthritis. Silicea produces inflammation of skin. It acts upon the constitution that are sluggish. There is i.perfect assimilation and defective nutrition. Presents with neurasthenic states and increased susceptibility to nervous stimuli. Presents with moist erruptiions on skin with fomation of scales. Usually patient presents with weak spine, susceptible to draught on back. Pain in coccyx. Diseases of bones of spine.
MEDORRHINUM
Medorrhinum is a nosode prepared from gonorrhoeal virus. It is a powerful deep acting remedy indicated for most of the cgronic complaints. Medorrhinum is a very valuable remedy for arthritic and rheumatic pains , loss of power in joints, joints feel loose. Useful in chronic psoriatic arthritis wuth great disturbance and irritabilty of nervous system. Pain in back with burning heat. Legs feel heavy and ache all night. Acting on skin medorrhinum causes intense itching worse at night. Yellowish copper coloured spots remain after erruptions.
ACTEA SPICATA
Actea spicata is a rheumatic remedy especially affecting the smaller joints, tearing tingling pain. Presents with wrist rheumatism. Though wrist is affected prominently other joints are too equally affected. Slight fatigue causes swelling of joints. Psoriatic erruptions on skin which are dry scaly and with intense itching.
SYPHILLINUM
Syphilinum is another nosode prepared from syphilitic virus. Acts on the bone, nerves, mucus membrane. Indicated in psoriatic arthritis. Presents with rheumatic stiffness and lameness in back. Aching in the whole spine. Inflammation of joints. Pains are usually aggravated by warmth of bed. Indiacted in shifting rheumatic pains and chronic eruptions like psoriasis, presents with dry scaly or pustular erruptions on different parts of the body in patches. Presents with great weakness with very few symptoms, utter prostration and debility in morning or on walking.
THUJA OCCIDENTALIS
Thuja has main action on the skin, bones. Useful in case of psoriatic arthritis. Thuja chiefly acts on the mucus membrane of skin, nerves, glands. Presents with cracking in joints when stretching them. Limbs feel as uf made of wood or glass and would break easily. Psoriatic erruptions itch or burn violently. Erruptions on covered parts of the body. Worse from scratching. Dry skin with brownish spots and scales with severe itching.
ALSO READ
Psoriasis
ARTHRITIS (GENERAL)
Rheumatoid Arthritis
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS
GOUT