Reactive Arthritis was also called Reiter’s Arthritis is RF-negative and HLA-B27 Linked Imflamatory oligoarthritis typical with Enthesitis, accompanied with Inflamatory occular and/or inflamatory genitourinary and other systemic manifestation usually post gastrointestinal or genitourinary infection.
During world war one and two many cases emerged with the Triad of Symptoms viz. Inflamation of Joints, Inflamation of eyes and Inflamation of Uretha. Which drew attention of medical community due to common presentation in many giving it some syndrome like picture. On further investigations it was found out that most of them were exposed to urogenital or Gastro-intestinal infection 1-4 weeks prior to onset of this Triad of Symptoms. This was initially termed as “Fessenger-Leroy-Reiter’s Syndrome” or simply “Reiter’s Syndrome”. But as the physician Hans Conard Julius Reiter was involved in attrocities and war crimes with Hitler, so his name was removed and later renamed and termed as “Reactive Arthritis”.
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF REACTIVE ARTHRITIS
- AGE – It more frequently affects age group of 20-40 years.
- SEX – It is more common in Males then in Females.
- ETHNICITY – Due to its association with HLA-B27 it is frequently found in white race compared to dark race as comparatively HLA-B27 occurs more commonly in white population.
- RISK FACTOR – Person with HIV positive status are more prone to develop reactive arthritis.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF REACTIVE ARTHRITIS
The onset of symptoms of Reactive Arthritis typically starts 4-35 days after an initial infection of gastro-intestinal system or genito-urinary system.
TRIAD OF REACTIVE ARTHRITIS
Reactive arthritis in most of the cases presents where patient cant – SEE, PEE, climb the TREE! due to following Classical Triad of Symptoms of reactive arthritis
i) OLIGOARTHRITIS
Oligoarthritis involving less than five joints. It may frequently involve knee and sacroilliac joint as well. May present itself in additive pattern where it starts with one joint and add another joints subsequently or it may be migratory in pattern where the set of inflamed joints keep changing by addition and simultaneous substraction of joints involved.
ii) NON-GONOCOCCAL GENITOURINARY INFLAMATION
Inflamation of genitourinary system classically presents itself at the onset of the disease. Not always but in many its typically after initial sexual exposure. It presents as frequent burning micturation, uritheritis, prostatitis, balanitis in men and salpingitis, vulvitis and vaginitis in women.
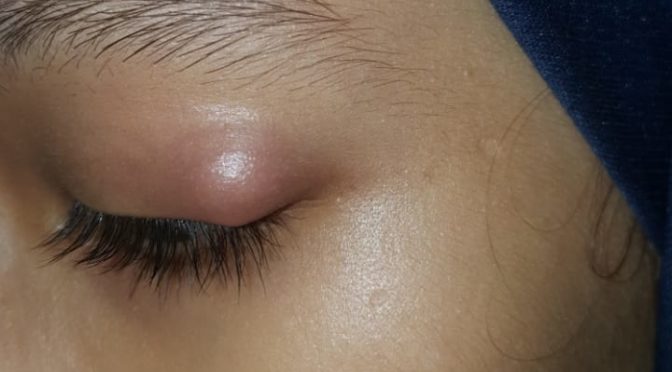
iii) OCCULAR INFLAMATION
Occular Inflamation may present itself as mild conjunctivitis or uveitis in 75% of cases with gastrointestinal origin and 50% of cases with urogenital involvement. patients have intermittent irritation in eyes with blurred vision typically commences at onset of disease.
OTHER SYMPTOMS
- Few patients also presents with peculiar symptom which is specific to reactive arthritis, its Keratoderma Blenorrhagica which are small hard nodule commonly appear on soles occasionally on palms and rarely on other parts of body subcutaneous nodules are not incluced. Even in absence of above mentioned triad of symptom the presence of Keratoderma Blenorrhagica is diagnostic for reactive arthritis.
- In reactive arthritis; typical to HLA B27 related immunological reactions; involves Entheses that is where skeletal muscles attaches with bones through tendons, where it causes Enthesitis and tendon inflamation especially the tendo-achilles and also fascia in particular Plantar Tendinitis.
- Occasionally patients also suffer from dactilitis giving finger sausage-like apperance “sausage finger” due to inflamation.
- Mucocutaneous involvement presents as ulcerative or non ulcerative stomatitis, apthous ulcers and geographic tongue are also seen as presentation of this disease
- Cardiac involvement causing pericarditis and aortic regurgitation in cases which do no recover soon or if its recurring or progressive.
- Gastrointestinal manifestation like pain and cramps with frequent semiformed stools with mucous and insome cases blood due to inflamation and ulcceration in gastrointestinal tract.
Most of the cases of Reactive Arthritis recover within six months, in many cases it keeps comming back time and again and in few it becomes chronic and progressive which may increase risk of severe complications.
COMPLICATIONS OF REACTIVE ARTHRITIS
In chronic progressive and recurring cases the patient may develop following complications
- Ankylosing Spondylosis
- Disabling Arthritis
- Aortitis
- Aortic Regugitation
- Conduction defects of Heart
- Pericarditis
- Amyloid deposits
- Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy
CAUSE OF REACTIVE ARTHRITIS
Reactive Arthritis is is HLA B27 linked inflamatory arthritis and enthesitis preceeded by a spell of infection either of genito-urinary system or gastro-intestinal system by following commonly involved organisms
GENITO-URINARY INFECTIONS ASSOCIATED WITH REACTIVE ARTHRITIS
- Chlamydia Trachomatis
- Ureaplasma Urealyticum
GASTRO-INTESTINAL INFECTIONS ASSOCIATED WITH REACTIVE ARTHRITIS
- Salmonella Spp.
- Shigella Spp.
- Campylobacter Spp.
- Yersinia Spp.
4-35 days after the spell of urethritis or food poisoning by above mentioned organisms the symptoms of reactive arthritis sets in, where the synovial fluid has negative culture ans is free from infection and but the HLA B27 linked inflamation is thought to be triggered due to
- Autoimmune reaction due to cross reactivity of micro-organism antigen with joint tissue or
- Micro-organism antigenic components that may have settled in joint tissue.
DIAGNOSIS OF REACTIVE ARTHRITIS
Clinically the Reactive Arthritis can be diagnosed with help of Sensitivity and Specificity Guidlines laid down by American College of Rheumatology, for clinical diagnosis with given set of presenting symptom, its as follows
- Arthritis > 1 month with Urethritis and/or cervicitis has sensitivity of 84.3% and specificity of 98.2%.
- Arthritis > 1 month with Urethritis or Cervicitis or bilateral Conjunctivitis has Sensitivity of 85.5% Specificity of 96.4%.
- Arthritis, Urethritis and Conjunctivitis has Sensitivity of 50.8% and sensitivity of 98.8%.
- Arthritis > 1 month, Conjunctivitis and Urethritis has Sensitivity 48.2% and Specificity of 98.2%.
Patients falling in above criteria or those showing just Keratoderma Blenorrhagica without any other symptoms and other suspected cases can be sent for following test for further evaluation.
- HLA B27 testing
- Urine routine and culture
- STOOL Routine and culture
- Cervix and Urethral swab culture
- Erythrocytes Sedimentation Rate
- C-Reactive Protein Test
HOMEOPATHIC TREATMENT FOR REACTIVE ARTHRITIS
Being an immune mediated systemic reaction that too the one that is triggered with different causative agents and even to same agents different individuals will respond differently.
Though they may have same set of general symptoms like the classical triad of reactive arthritis but intensity of each of the symptom of triad will differ in each individual,
Now this is where the homeopathic individualisation process starts. In Homeopathy we believe that though majority of human genome is the same but the minor variations in gene and the epigenome make the whole lot of difference in various characteristerics of each individual, similarly their immune reaction also varies, so every person should have individualised medicine.
Homeopathic Treatment is based on symptom similarity and individualisation of case based on peculiar symptoms based on which the case is individualised and medicine is selected.
Alternatively as per Homeopathic principle of Genus Epidemicus or pathology based symptomatology there can be disease specific homeopathic medicine derived from common symptomatic representation of a disease condition in a group of population.
Now this can not be the most similimum homeopathic prescription but roughly it can hit the disease condition within an indivudual though not accurate but will yeild some results in most of the cases.
To yield best homeopathic results there can be no generalised common approach for all cases.
But still if we have to attempt common standardised pathology based approach then to give some guidelines on homeopathic approach towards cases of reactive arthritis I have attempted following rough guidelines which may help to give some vision in approach towards such cases.
Its seen that in few case it begins after gastro-intestinal infection and in some case post genito-urinary infection. So this will further guide determining “morbid cause” behind the disease directing us in homoeopathic similimum medicine selection.
Now reactive Arthritis shows a triad of symptom in most of the cases. So this triad helps us to reach to group of medicines with such combination of symptoms.
Intensity, occurance of symptoms and its sequence in triad differs in each individuals. For example
- In some person urogenital symptoms may be more severe compared to occular symptoms or arthritis symptoms, where as in others arthritis and ocular symptoms would be more severe than urogenital symptoms.
- Some may not have occurence of conjunctivitis
- In some all three triad occur at a time where as in some patients it may occur gradually one after another in different sequence.
All this helps us find out the “seat of disease” in an individual and its degree of affinity towards various organs which can be related to homeopathic medicines during selection process.
Further arthritis may show different pattern like
- progressive
- migratory
- additive
- symetry
- predominantly involved joint
- sequence of joint involvement
- number of joints involved
- severity
- intensity
- type of sensation and other symptoms
Also similarly symptoms of occular involvement and urogenital involvement should be take in to account in absolute detail. This further helps refine and classify the patient and the respective medicines to be repertorised.
Which other systems and organs are involved like mucous membranes, skin, heart, kidney etc and what type of pathology they are showing like tissue destruction or just inflamation and functional disturbance or tissue lysis with regenerated and degenerative changes this will help to decide what “type of miasm” is underlying wether its psoric, syphillitic or psychotic type pathology.
Certain symptom are very “peculiar” for the disease and occurs in few individuals like Keratoderma Blenorrhagica eruption, now location of this eruption will further help individualise the case.
Enthesitis – Inflamation of tendo-achilles and plantar fascitis is “very specific” to the disease but does not occur in all individuals, so if plantar fascitis or inflamation of tendo-achilles if occurs in someine with this disease then it helps further in individualisation of during homeopathic medicine selection.
Other than this the general health and family background should be noted to derive constitutional types and association of HLA B27 in 75% of this individual further helps in individualisation and homeopathic medicine selection.
COMMONLY USED HOMEOPATHIC MEDICINES FOR REACTIVE ARTHRITIS
- PHOSPHORUS
- ARSENICUM ALBUM
- RHUS TOXICODENDRON
- BRYONIA ALBA
- LEDUM PALUSTURE
- THUJA OCCIDENTALIS
- ANTIMONIUM CRUDUM
- ARGENTUM NITRICUM
- BORAX
- MERCURIOUS SOLUBILIS
- PULSATILLA NIGRICANS