Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic systemic auto-immune disorder predominantly affecting synovial joints.
Rheumatoid Athritis may also affect tissues other than those in joint; like blood, skin, pleura, lungs, kidney, nerves, heart, pericardium, blood vessels, eyes, liver etc.
CAUSES OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA)
It is still unclear how it is caused but it is believed to be combination of
1) Genetic Factors
HLA-DR4 – HLADRB1 is storngly associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis but not in all ethnicity it shows the same significance.
MHC class II related allotypes and T-cell Associated Protein PTPN22 are also found to be associated with RA.
2) Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Environmental factors like radiations, pollution etc. Exposure to fine crystalline form of pure silica i.e. Silicon Dioxide can cause Rheumatoid Arthritis, is an established fact.
Lifestyle factors like addiction to cigarette smoking, mental stress, physical stress and digestive disturbances are also doubted (though unconfirmed).
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, hormonal medications etc. are also believed to be strong contributing factors.
Still we are not able to link any infectious agent or vector associated to RA.
PATHOGENESIS AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA)
It has been observed that there is an abnormal immune response, where in, there is a state of persistent cellular activation, due to constant positive feedback (probably due to inhibition of negative feedback pathway or exaggerated positive feedback due to certain factors) causing formation of immune complexes and autoimmunity. This initially shows up in synovial joint and less frequently or later in other organs and tissues as well.
Rheumatoid Arthritis manifests in following phases :-
- Initial phase – shows non-specific inflamation
- Amplification phase – caused by T-cell activation
- Chronic inflamatory Phase – where Cytokines like Interlukine-1 Interlukine-6 Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha comes in picture causing chronic inflamation and tissue injury
Antibodies to IgGFc are called Rheumatoid Factor (RF/ RA factor) and Antibodies to Citrulinated Peptides (ACPA) are major factors specific in pathology of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Other nonspecific factors are abnormally Glycosylated Antibodies. These are believed to be the contributing factors in arthritis. Though they are not specific to Rheumatoid Arthritis and are also present in many other Autoimmune conditions.
B lymphocytes → Plasma cells → RA factor and ACPA(of IGg And Igm Classes) + Fc receptors & compliment (binding due to antibody’s altered N glycans) (simultaneously; doubted TNF activation at this Stage) → Macrophage activation → Synovial macrophage & dendritic cells further expresses MHC class II molecules → Synovial oedmatous inflamation with T cell activation(also doubted TNF activation through T cell product IL17) and infiltration(mainly CD4 and CD8) → Intense inflamation – Granulation tissue formation -Angiogenesis – Inflamatory products damaging tissues – Thickening of synovium- Cartilage disintegration -Bone disintegration-Joint degeneration.
It is observed that presence of B-cell and T-cell at site is not necessary for the pathogenesis. So the exact role of B-cell and T-cell is doubted. Also TNF a major foctor responsible for progress of Rheumatoid Arthritis is doubted that wether its predominantly derived through B-cell or T-cell channel or through both as presented in above flow chart.
Other factors like IL1, IL6, IL15, IL17 are also believed to be important in pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Signs and Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
General Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Low Grade Fever not necessarily in all cases.
- Malaise
- Morning Stiffness
- Loss of appetite
- Weight Loss
Arthritis
Polyarthritis i.e. multiple joint involvement -small joints of hands, feet and spine are affected more than compared to larger joints like – knee, shoulder, hip joints but not always, in many patients, initially it may present as Monoarthritis ie single joint involvement.
Synovitis and erosion of joint tissue, tendinitis, with surrounding tissue swelling. It presents as swollen, tender, warm joints, causing stiffness and resulting into loss of range of motion of joint.
Morning stiffness difficultly in motion of affected joint with sensation of stiffness and pain. Morning stiffness lasts for more than an hour. Aggravation of pain and stiffness of joints on prolonged rest and ammelioration on motion is a distinguishing character of inflamatory arthritis like Rhuematoid Arthritis in its early stages, compared to non inflamatory conditions like osteoarthritis, where the causes are mechanical so it has motion aggravation and rest ammelioration and morning stiffness is not prolonged for more than an hour, pain is nociceptive and not neuropathic.
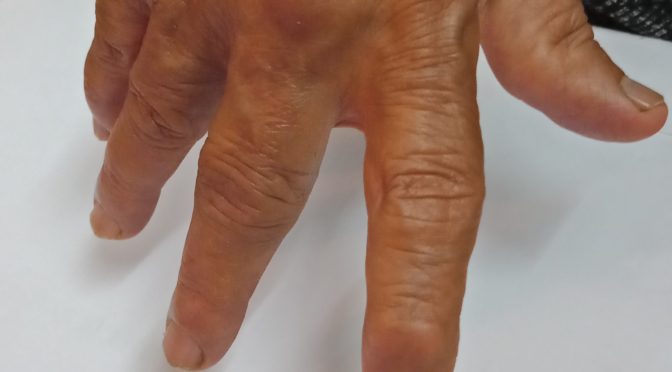
Various Deformities
- Necrotising Granuloma or Rheumatoid Nodule typically appears over areas where there is excessive mechanical stress, like bony processes or prominencies eg knuckles, wrist, elbow, heel etc, they are few milimeters to centimeter in diameter.
- Ulnar deviation of fingers.
- Button Hole Deformity or Boutonniere Deformity – proximal interphalangeal joints flexed and distal interphalangeal joints extended.
- Swan Neck Deformity flexed distal interphalengeal joint and proximal interphalengeal joint hyperextended
- Hammer Toe Deformity
- Z-thumb deformity or Z deformity the interphalengeal joint gets hyperextended and there is subluxation of metacarpo-phalengeal joint with fixed flexion.
- Arthritis Mutilans
- Atlanto axial subluxation due to erosion of odontoid process and transverse process which initially presents as clumsiness and may progress into quadripelgai and eventually death.
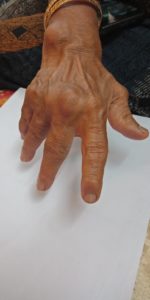
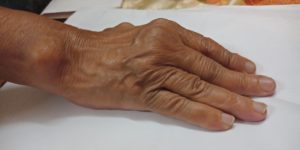
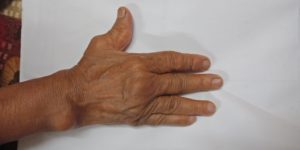
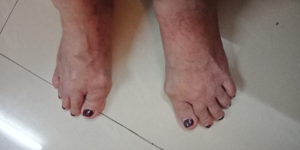
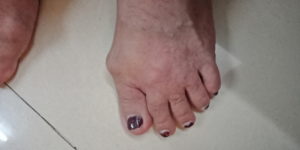
Skin Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Necrotising Granuloma or rheumatic nodule many a times appears in the skin.

Mononeuritis Multiplex caused due to severe Rhematic vasculitis and vasculitic nerve infarction of small and medium sized blood vessels also giving rise to skin ulcers
Occasionally the skin may also present with
- Pyoderma Gangrenosum
- Sweet’s Syndrome
- Erythema Nodosum
- Lobe Paniculitis
- Atrophy of finger skin
- Palmar Erythema
- Fragile Skin
Few of above complications are due to prolonged allopathic medication.
Lungs involvement
Fibrosis of lungs is well recognised consequence of allopathic treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Caplans syndrome, when RA pt gets exposed to coal dust it gives rise to rheumatoid lung nodules.
Pleural effusion is associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Cardiac involvement in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatiod Arthritis may affect heart and cause pericarditis, endocarditis, valvulitis, Left Ventricular Failure, Fibrosis.
Rheumatiod Arthritis significantly increases risk of artherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, stroke.
Most of the RA patients do not develop pain of angina or myocardial infarction so are at high risk to be left undiagnosed.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Affects major components of blood
In blood, Rheumatoid Arthritis causes Hepcidin levels to increase leading to Anaemia of Chronic Disease.
Leucocytopenia in patients with felty’s syndrome.
Neutropenia and Thrombocytosis if inflamation persists.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Affects Kidneys
Renal Amyloidisis is consequence of chronic inflamation of RA.
Allopathic treatment of RA may cause membranous nephropathy.
Eye Manifestation of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Episcleritis, Scleritis, Keratitis Keratoconjunctivitis, Scleromalacia, Keratomalacia, Xeropthalmia are occular complications of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Liver Complications in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Liver may be affected due to prolonged allopathic treatment of Rhuematoid Arthritis and if there are any other inflamatory Liver complaints or autoimmune conditions affecting liver, coexisting with RA, it can create complications in liver.
Neuronal Complications Due To Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA affects neurons to cause Peripheral neuropathy, Mononeuritis Multiplex, Carpel Tunnel Syndrome, Myelopathy due to Rheumatoid disease of spine. Atlanto-Axial subluxation due to erosion of odontoid process and transverse process which initially presents as clumsiness and may progress into quadripelgai and eventually death.
DIAGNOSIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA)
X-rays
X-rays may not show any changes in early stages though sometimes mild soft tissue swelling might be visible in later stages along with soft tissue swelling it may show juxta-articular osteopenia and loss off joint space in advanced stage it may also show nodes bony erosion subluxation of affected joints.
Blood Tests
Test for RA factor
Negative serological tests doesnt exclude the probablity of Rheumatoid Arthritis. As 20-25% of RA patients are negative for RA factor test which is considerably large number. Also during first year of development of rheumatoid factor majority of the patients are usually negative. 10% of healthy person may show positive for RA Factor. Even persons with Hepatitis C and persons with chronic autoimmune diseases like Systemic Lupus erythematosus or Sjogren’s syndrome may show positive RA factor test. So the test is not specific and also not much sensitive.
Test for ACPA (measured as Anti-CCP antibodies)
ACPA with 95% specificity is much more specific compared to RA factor test but has lower sensitivity only 60-70% compared to 80-85% of RA Factor test.
Patients with clinical features and all other investigations pointing towards Rheumatoid Arthritis except their RA Factor and Anti-CCP tests are negative sich patients are called seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis cases almost 25% cases falls in this category.
New point of care test is introduced where in; RF and anti-MCV are detected which has sensitivity of 72% and specificity of 99.7%
Other non-specific, indirect, additional supportive tests to RA factor and ANTI-CCP tests are :-
ESR; CRP; CBC; RFT; LFT; ANA; Ferritin levels.
DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATION CRITERIA FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
This diagnosis and classification criterion is jointly developed by American College of Rheumatology and European League Against Rheumatism has become widely accepted globally is as follows:
A Score of 1-10 is established by adding scores of following 4 different criteria
- Number and type of joints involved
- RA factor and ACPA tests
- Acute Phase Reactants CRP and ESR
- Duration of Disease
1) Score Rating of NUMBER and TYPE of JOINTS involved
- 1 Large joint = 0 points
- 2-10 Large Joints =1 point
- 1-3 small joints(with/ without Large Joint involvement) = 2 points
- 4-10 small joints(with/without Large joint involvement) = 3 points
- Involvement of more than 10 joints including atleast 1 small joint =5 points
2) Score Rating of Specific Serological Tests (RA factor and ACPA)
- Negative RA factor and ACPA = 0 points
- Low positive RA factor or Low Positive ACPA = 2 points
- High Positive RA factor or High positive ACPA = 3 points
3) Score Rating of Acute Phase Reactants
- Elevated ESR and CRP = 1 point
4) Score Rating of Duration of disease
- Duration of Arthritis if more than 6 months =1 point
A score of 6 or above establish positive Rheumatoid Arthritis as diagnosis.
HOMEOPATHIC ARTHRITIS MANAGEMENT
Homoeopathic Arthritis Management depends on individualisation of the patient based on present symptoms, past history, family history and constitution of the patient.
In arthritis cases it is necessary to take into account the following points (with constant search for underlying miasm and constitution type):
- When it started, that is since how long its been there.
- How was the onset when it appeared first time.
- Wether the complaints had incidious progression or it was sudden.
- Which joint is involved, wether its single joint or multiple, wether its bilateral and symetrical or diagonal.
- Particulars like which part was affected first, which side it started first and how much time it took for progression to other side or other joints, sequence in which joints were involved.
- How and when it gets triggered, aggravation pattern morning stiffness , aggravation on rest/ motion, relation to climate winter/monsoon/summer, relation to heat and cold, aggravation to any particular type of food.
- Wether its constant or intermittant.
- The joint is warmer than rest of the body or not.
- Wether there is swelling around the joint or not.
- Nodes or nodosities on or around any joints. or any other signs of disfigurement.
- Movement or other disability in joint.
- Patient has fever or not or h/o fever before or during the episode of joint pain started.
- Presence of any concomittants or accompanying symptoms and wether those symptoms are of Psychotic, Syphilitic or Psoric nature.
- Wether he has any other systemic complaint especially any other autoimmune or metabolic disorder.
- History of injury, surgery especially affecting neurons or musculoskeletal structure.
- Nature of work the patient does , postural habits, structural anomalies disfigurements.
- Diet sleep and exercise routine water intake should also be noted carefully.
- It is important to note family history of patient wether first degree relative had any autoimmune or metabolic disorder.
- Wether patient was or is under any long term medication.
A careful history of all communicable ailments should be recorded in sequence as they had been contracted by patient, as it helps us evaluate when and how was the vital force deranged in past and wether the present condition is manifestation of some past ailment, that is any deep seated miasm, also it helps to establish wether its some inherited genetic condition or its acquired condition also it helps differentiate between
- Vector borne conditions like post viral arthralgia/arthritis and Group A streptococcal borne post pharyngitis systemic autoimmune condition.
- Other Systemic autoimmune conditions like Rheumatoid Arthritis SLE psoriatic arthritis.
These basic question will lead you towards a broader vision in the case and will let you reach upto some conclusion that under what category of arthritis it should be classified and will lead you towards some understanding of miasm and constitution.
As I have mentioned in my other arthritis articles that basically I divide all types of arthritis into four major categories based on their pathogenesis.
- Mechanical
- Immunological
- Metabolic
- Septic
After being diagnosed and classified the disease condition from one of the above group we can go further on how to manage each type of case.
Rheumatoid Arthritis falls under immunologically mediated arthritis.
Once established that its an immune mediated arthritis its necessary to rule out any damage to other organs like heart, liver, kidney, pancreas, eyes etc, as in most cases autoimmune arthritis is found to involve other system and organs or it is a part of broader systemic autoimmune condition and it is all the more necessary to find out miasmatic background, constitution and individualising symptoms, as such types of arthritis are deep seated having its own sets of aggravating and ammeliorating factors, furthermore its also observed that mental stress and emotional fluctuations have much impact on intensity and frequency of aggravations in almost all types of immunologically mediated arthritis, so its of utmost importance to take proper account of patient’s mental emotional past and present including likes and dislikes aversion and cravings, which helps us to individualise the case.
Once the we have derived constitution , miasmatic background and individuslised the case then comes medicine selection process.
I strongly recomend to go by constitution of patient in immunologically mediated arthritis rather than going theraputic remedy selection.
It should be kept in mind that the selection procedure of medicine should correspond to degree of mental PQRS , degree of systemic PQRS and degree of musculo-skelatal symptoms of the person in disease should match the degree of pathogenic action on various sphere of the specific medicine.
Though during acute exacerbations of disease it becomes necessary many a times to administer short acting acute medicines theraputically where the new symptoms desnt fall into sphere of the constitutional medicine thats been administered.
Many a times only a single dose of similimum medicine selected may suffice to cure the case but all patients are not the same. As each case has a different constitution, miasmatic background, severity of ailment and other external inimical factors. So in many cases before it gets cures, it may require series of medicines one after another as per case demands during progression of treatment. It all depends upon how well the physician is able to find out the similimum and type of case and its requirement.
HOMEOPATHIC MEDICINES FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Though the approach should always be constitutional in autoimmune disease like rheumatoid arthritis, there are certain medicines which broadly shows pathological drug picture of rheumatoid arthritis or striking peculiar so could be used as therapeutic guidance.
- SILICEA – Rheumatoid Arthritis post exposure to fine crystalline form of silica ie silicon dioxide (an established factor that contributes in development of rheumatoid arthritis).
- RHUS TOXICODENDRON – While repertorising I have frequently ended up Selecting this remedy in final roundction during conditional approach. Rheumatoid Arthritis has stiffness of joints on prolonged rest especially in morning last more than an hour and gradually ameliorating on motion. Rhus tox has common symptom of aggravation on rest and amelioration on motion and also this medicine has great affinity towards joints and immune mediated disorders.
- LEDUM PALUSTURE – This homeopathic medicine has always given me good results in any type of inflammatory joint complaints with swelling and redness especially around ankles.
- APIS MELIFICA – I use this medicine with great results during active phase of disease where patient has developed swelling and redness with severe pain just like Ledum pal but more severe acute and sudden in onset.
- CALCAREA CARBONICA – Can be used as complimentary medicine during the course of the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis especially in later stages where patients starts showing symptoms of bone erosion and reduced bone mineral density around articular surface due to prolonged inflammation and chronic autoimmune condition in body.
- GUALTHERIA PROCUMBENS – In my experience gaultheria yields good results good results; usually in low potency and mother tincture forms; during active exacerbation of disease where in patients joint pains rheumatoid arthritis aggravates on disturbed digestion and other gastric ailments.
- SYPHYLLINUM – indicated in later stages where patient starts showing signs of destruction of tissue, degeneratation and disfigurement and necrotising granulomatous nodules of lungs skin and bones. Especially in cases of rheumatoid arthritis with history of syphilis(treponema pellidum) infection this nosode should be administered
- TUBERCULINUM – Patients with rheumatoid arthritis if exposed to coal for longterm, they typically develop necrotizing granulomatous nodule in lungs in such condition this medicines comes in to aid in such rare peculiar symptom. Also it should be thought of in patients with necrotising granulomatois nodule of rheumatoid arthritis on bones and skin.
- DULCAMARA – this remedy should be thought of when Rheumatic complaints tend to increase in damp cold weather.
- BELLADONNA – inflammation of joints during acute exacerbation of RA.